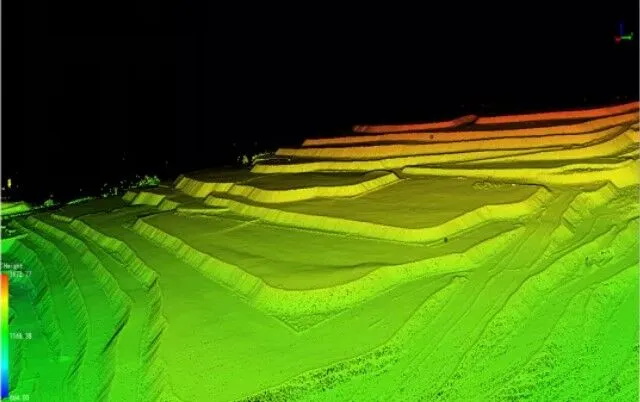
Terrain mapping is a critical component of various industries, including construction, mining, forestry, and environmental management. Accurate and detailed maps are essential for planning, monitoring, and decision-making. Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology has emerged as a powerful tool for terrain mapping, offering a range of advantages over traditional surveying methods.
High Precision and Accuracy
One of the most significant advantages of LiDAR surveys is their high precision and accuracy. LiDAR systems use laser pulses to measure distances to the Earth’s surface, creating highly detailed and accurate 3D models of the terrain. This level of precision is particularly valuable in applications where even small errors can have significant consequences, such as in the design of infrastructure projects or the assessment of natural hazards.
Rapid Data Collection
LiDAR surveys can cover large areas quickly, making them an efficient option for terrain mapping. Traditional surveying methods, such as ground-based surveys, can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. LiDAR systems, particularly those mounted on drones or aircraft, can capture data over vast areas in a fraction of the time. This rapid data collection allows for quicker decision-making and more timely project implementation.
Ability to Penetrate Vegetation
One of the unique advantages of LiDAR technology is its ability to penetrate vegetation and capture data about the underlying terrain. This capability is particularly valuable in forestry and environmental management, where understanding the topography beneath dense vegetation is essential. Traditional surveying methods often struggle to provide accurate data in such environments, but LiDAR can effectively “see through” the vegetation, providing detailed information about the ground surface.
Versatility and Flexibility
LiDAR systems are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of environments and applications. They can be mounted on drones, aircraft, or ground-based vehicles, making them suitable for various terrains and conditions. This flexibility allows for the customization of LiDAR surveys to meet the specific needs of different projects, whether it’s mapping a rugged mountain range or a dense urban area.
Enhanced Data Analysis
The data collected by LiDAR systems can be analyzed using advanced software to create detailed 3D models, contour maps, and other visualizations. These models can be used to identify features such as slopes, drainage patterns, and potential hazards, providing valuable insights for planning and decision-making. The ability to analyze and visualize data in such detail is a significant advantage over traditional surveying methods.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in LiDAR technology may be significant, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. LiDAR surveys can reduce the need for extensive ground-based surveys, which can be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, the rapid data collection and analysis capabilities of LiDAR can lead to more efficient project planning and implementation, reducing overall costs.
Environmental Benefits
LiDAR surveys also offer environmental advantages. Traditional surveying methods, particularly those involving extensive ground-based activities, can have a significant environmental impact. LiDAR systems, particularly those mounted on drones, have a much smaller environmental footprint. This makes them a more sustainable option for terrain mapping, particularly in sensitive or protected areas.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology is revolutionizing the field of terrain mapping, offering a range of advantages that support more accurate, efficient, and sustainable data collection. From high precision and rapid data collection to the ability to penetrate vegetation and enhanced data analysis, LiDAR surveys are proving to be an invaluable tool for various industries. As technology continues to advance, the role of LiDAR in terrain mapping is set to expand, paving the way for more informed and effective decision-making in a wide range of applications.